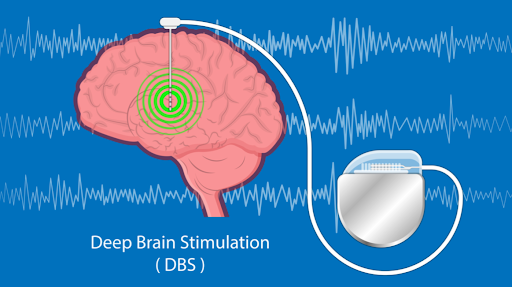
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical intervention that involves the implantation of a medical device, a neurostimulator, in the brain to regulate abnormal neural activity. This medical device is connected to electrodes that are placed in specific areas of the brain, and it delivers electrical impulses that help to modulate the abnormal activity and restore normal brain function. Deep Brain Stimulation Systems have been proven to be an effective treatment option for a variety of neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of DBS systems, including the technology behind them, patient selection criteria, the surgical procedure, and the benefits and risks associated with them.
Technology behind DBS Systems
DBS systems consist of three main components: the neurostimulator, the electrodes, and the programming system. The neurostimulator is a small device that is implanted under the skin, usually in the chest area. It generates the electrical impulses that are delivered to the brain through the electrodes. The electrodes are thin wires that are inserted into specific areas of the brain, depending on the type of disorder being treated. Finally, the programming system is used to adjust the settings of the neurostimulator, to ensure that the electrical impulses are delivered at the right intensity and frequency.
Patient Selection Criteria
Not all patients with neurological disorders are suitable candidates for DBS systems. Patient selection criteria vary depending on the type of disorder being treated, but in general, patients should have a clear diagnosis of the disorder, and they should have tried other treatment options without success. Additionally, patients should have no significant cognitive or psychiatric issues that could affect their ability to comply with the treatment regimen, and they should have no medical conditions that could increase the risks associated with the surgery.
Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for DBS systems is performed under general anesthesia, and it typically involves three main steps. First, the electrodes are inserted into the brain, using a stereotactic frame that helps to guide the surgeon to the target area. Second, the neurostimulator is implanted under the skin, usually in the chest area. Finally, the electrodes are connected to the neurostimulator, and the programming system is used to adjust the settings of the device. The whole procedure can take several hours, and patients are usually discharged from the hospital after a day or two.
Benefits and Risks Associated with DBS Systems
DBS systems have been shown to be an effective treatment option for a variety of neurological disorders, and they can significantly improve the quality of life for patients who suffer from them. For example, patients with Parkinson’s disease who undergo DBS can experience a reduction in tremors, stiffness, and other motor symptoms. Similarly, patients with essential tremor or dystonia can experience a reduction in involuntary movements. DBS systems can also reduce the severity of symptoms in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder.
However, like any surgical intervention, DBS systems carry some risks. These risks include infection, bleeding, stroke, and hardware failure. Additionally, patients may experience side effects from the electrical impulses, such as tingling, numbness, or muscle contractions. These side effects can usually be managed by adjusting the settings of the neurostimulator.
Conclusion
DBS systems are an innovative and effective solution for a variety of neurological disorders. They offer patients a chance to improve their quality of life by reducing the severity of their symptoms. However, DBS systems are not suitable for all patients, and they carry some risks. Patients who are considering DBS should discuss the benefits and risks with their healthcare provider, and they should carefully consider their options before making a decision.